Keeping up with rapid technological advancements can be overwhelming. Many struggle to understand the role of Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs) in our increasingly automated world. This knowledge gap can lead to missed opportunities and inefficiencies in various industries.
Fortunately, this comprehensive guide demystifies IEDs, their applications, and their impact on sectors like manufacturing, energy, and home automation. By exploring the core concepts, benefits, and future trends of IEDs, you’ll gain valuable insights to navigate the evolving landscape of smart technology and make informed decisions for your business or personal use.
Historical Context and Evolution
Smart devices have come a long way since the 1960s. Early versions were simple control units. By the 1980s, they got smarter with microprocessors. The 1990s saw networked devices emerge. In the 2000s, Intelligent Electronic Devices became common in many industries. Today, these gadgets are more powerful than ever. They can do complex tasks and work together seamlessly.
Key Components of Intelligent Electronic Devices
These smart gadgets have several important parts. The brain is a powerful computer chip. Sensors act like eyes and ears, collecting data. Memory stores information. Communication tools let the device talk to other machines. Software tells the device what to do. A power supply keeps everything running. All these parts work together to make the device smart and useful.
Functionality and Capabilities of IEDs
Intelligent Electronic Devices can do many impressive things. They monitor systems closely and react quickly to changes. These devices can control other machines precisely. They analyze data to spot trends and predict problems. Many can learn and improve over time. Some even make decisions on their own. Their abilities help make work safer and more efficient in various fields.
Data Collection and Processing
Smart devices are great at gathering information. They use sensors to measure things like temperature, pressure, or movement. The devices then sort through this data quickly. They can spot important patterns or issues. Some even use fancy math to make sense of complex information. This helps businesses make better choices based on real facts.
Applications of Intelligent Electronic Devices
These smart gadgets are used in many areas. Factories use them to control machines. Power companies use them to manage electricity. Homeowners use them to make their houses smarter. Doctors use them to monitor patients. Farmers use them to water crops. Even cars use them to drive safer. Intelligent Electronic Devices are helping in almost every part of our lives.
Industrial Automation and Control
Factories are getting smarter thanks to Intelligent Electronic Devices. These gadgets control robots and machines. They keep production lines running smoothly. If something goes wrong, they can fix it quickly. They also track how much is being made. This helps factories make more stuff with less waste. Workers can focus on important tasks while the devices handle routine jobs.
Smart Grid and Power Systems
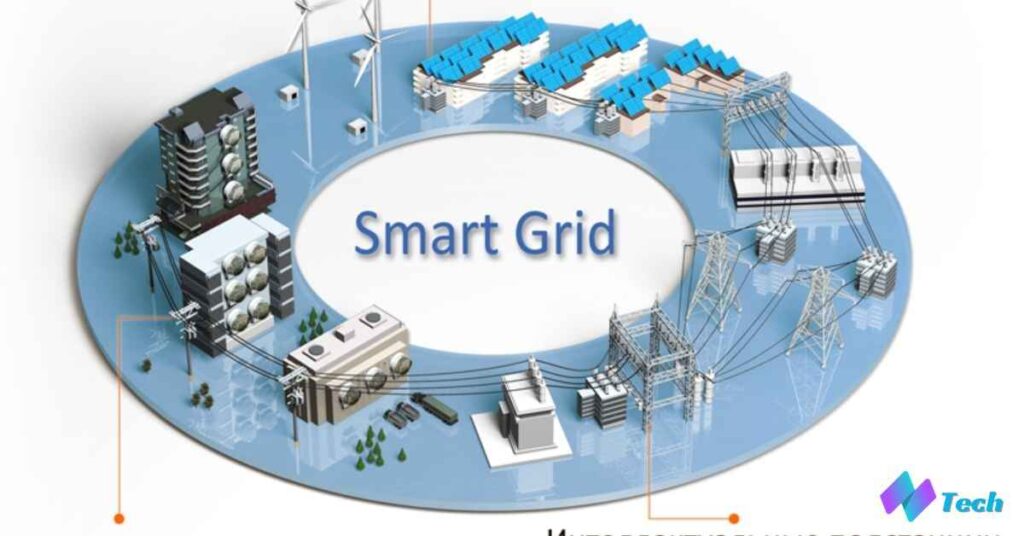
Intelligent Electronic Devices are making our power systems smarter. They help manage the flow of electricity. These devices can detect problems in power lines quickly. They also help balance power supply and demand. When there’s extra power from solar or wind, they can store it. During peak times, they can reduce usage in some areas. This makes our power grid more reliable and efficient.
Home Automation and IoT
Our homes are getting smarter with Intelligent Electronic Devices. Smart thermostats learn when to heat or cool. Security cameras can tell the difference between people and animals. Voice assistants can control lights and play music. Smart fridges can order groceries. All these devices talk to each other through the internet. They make our homes more comfortable, safe, and energy-efficient.
Transportation and Logistics
Intelligent Electronic Devices are changing how we move people and goods. In cars, they help with navigation and safety features. Trucks use them to plan the best routes. Ships and planes use them for navigation. In warehouses, these devices track packages. They help companies know where everything is at all times. This makes travel safer and shipping faster.
Benefits of Implementing Intelligent Electronic Devices
Using these smart gadgets brings many good things. They help save money by using less energy. Work gets done faster and with fewer mistakes. They can spot problems before they become big issues. This means things break down less often. They also make work safer for people. Intelligent Electronic Devices help businesses run smoother and grow faster.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity

Intelligent Electronic Devices help get more work done. They can work 24 hours a day without getting tired. These gadgets do repetitive tasks quickly and without mistakes. They free up people to do more important jobs. In factories, they keep machines running at the best speed. On farms, they water crops only when needed. This means less waste and more output.
Enhanced Safety and Reliability
Safety gets better with Intelligent Electronic Devices. In factories, they can shut down machines if something’s wrong. On roads, they help cars avoid crashes. In buildings, they can detect fires early. These devices also make things more reliable. They can predict when a machine might break. This allows for fixes before big problems happen. All this keeps people safer and systems running smoothly.
Cost Reduction and Resource Optimization
Intelligent Electronic Devices help businesses save money. They use energy more wisely, cutting power bills. These gadgets reduce waste by using just the right amount of materials. They also spot problems early, preventing costly breakdowns. In factories, they keep machines running at peak efficiency. On farms, they help use water and fertilizer more effectively. This means companies can produce more while spending less.
Improved Data Analytics and Decision Making
Smart devices are great at handling lots of information. They collect data from many sources and make sense of it quickly. This helps managers make better choices. For example, a store might use these devices to track what sells best. A farm can use them to decide when to plant crops. Intelligent Electronic Devices turn raw data into useful insights, making it easier to run businesses smoothly.
Read This Blog: Top 21 Real Estate Investment Companies in the US: Uncover Lucrative Opportunities
Challenges and Considerations in IED Implementation
Bringing in Intelligent Electronic Devices isn’t always easy. It can cost a lot of money at first. Some workers might worry about losing their jobs. Old systems might not work well with new devices. There’s also a need to train people to use them. Security is another big concern. Companies need to plan carefully to overcome these hurdles and get the most out of smart devices.
Security and Privacy Concerns
Keeping Intelligent Electronic Devices safe from hackers is crucial. These gadgets often handle sensitive information. A security breach could lead to stolen data or system shutdowns. There’s also worry about privacy. Smart devices collect lots of data about how we live and work. Companies need strong safeguards to protect this information. Balancing the benefits of smart devices with security needs is an ongoing challenge.
Interoperability and Standardization
Getting different smart devices to work together can be tricky. Each company might use its own system. This can lead to devices that don’t communicate well. It’s like trying to fit puzzle pieces from different sets. The industry is working on common standards. These are like rules that all devices should follow. Intelligent Electronic Devices that speak the same language will work better together, making systems more efficient.
Skill Gap and Training Requirements
Working with Intelligent Electronic Devices requires new skills. Many workers need to learn how to use and maintain them. This can be challenging, especially for older employees. Companies often need to provide training. Some schools are starting to teach these skills too. As smart devices become more common, having these skills becomes more important. It’s an ongoing process to keep up with new technology.
Ethical Considerations
Using Intelligent Electronic Devices raises some big questions. We need to think about how they affect privacy and jobs. There’s worry about machines making important decisions. We must ensure these devices are used fairly and don’t discriminate. There’s also the question of who’s responsible if something goes wrong. As we use more smart devices, we need to consider these ethical issues carefully.
Also Read: Top 23 Real Estate Development Firms Shaping the US
Future Trends in Intelligent Electronic Devices
The future of smart devices looks exciting. They’re getting smaller, faster, and smarter. Soon, they might be able to learn and improve on their own. We’ll see them in more places, from our clothes to our cities. Intelligent Electronic Devices will work together more smoothly. They’ll help us solve big problems like climate change. The line between the digital and physical worlds will blur even more.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
AI is making Intelligent Electronic Devices even smarter. These gadgets can now learn from experience, just like humans. They can spot patterns we might miss. In factories, they can predict when machines need fixing. In homes, they learn our habits to save energy. AI helps these devices make better decisions on their own. This means they can handle more complex tasks without human help.
Edge Computing and Distributed Intelligence
Edge computing is changing how Intelligent Electronic Devices work. Instead of sending all data to a central computer, devices can process information on the spot. This makes them faster and more reliable. It’s like having a smart brain in every device. They can make quick decisions without waiting for instructions. This is especially useful in places with poor internet connections or where speed is crucial.
5G and Advanced Connectivity
5G networks are supercharging Intelligent Electronic Devices. This new technology allows devices to communicate much faster. They can share more information in real-time. This opens up new possibilities, like remote surgery or self-driving cars. 5G helps smart cities run smoother. It allows for better coordination between devices. With 5G, Intelligent Electronic Devices can do more complex tasks and work together better than ever before.
Sustainability and Green Technology
Intelligent Electronic Devices are helping the planet. They make buildings use less energy. Smart irrigation systems save water on farms. In factories, these devices reduce waste. They help cars drive more efficiently. Solar panels work better with smart controls. These gadgets even help track and protect wildlife. By using resources wisely, they’re making our world greener.
Building the Future of Manufacturing with IEDs
Factories are changing fast with Intelligent Electronic Devices. Machines now talk to each other. They can adjust production on their own. Workers use tablets to control entire production lines. These devices spot problems before they happen. They help make custom products easily. Factories are becoming smarter, safer, and more flexible. This new way of making things is called smart manufacturing.
Industry 4.0 and Smart Factories
We’re in a new age of manufacturing called Industry 4.0. Intelligent Electronic Devices are at its heart. They connect machines, products, and people. Factories can now make decisions on their own. They adapt quickly to new orders. These smart factories use data to improve constantly. They’re more efficient and can make custom products easily. This revolution is making manufacturing faster and smarter than ever.
Predictive Maintenance and Asset Management
Intelligent Electronic Devices are changing how we care for machines. They listen to equipment and spot problems early. This means fixing things before they break. It’s like giving machines check-ups. These devices track when parts wear out. They help plan repairs at the right time. This keeps factories running smoothly. It saves money and time by avoiding big breakdowns.
Quality Control and Process Optimization
Making good products consistently is easier with Intelligent Electronic Devices. They check quality at every step. If something’s not right, they fix it fast. These devices learn the best way to make things. They adjust machines to work better. This means fewer defects and less waste. Products turn out great, and customers are happier. Factories can make more without losing quality.
FAQ
What’s the difference between an IED and a regular electronic device?
IEDs can make decisions and adapt. Regular devices follow fixed programs.
Are all IoT devices considered Intelligent Electronic Devices?
No, not all. IoT devices connect to the internet, but may not be “intelligent”.
How do Intelligent Electronic Devices impact data privacy?
They collect lots of data, which needs careful protection to ensure privacy.
What skills are needed to work with Intelligent Electronic Devices?
Programming, data analysis, and understanding of specific industry processes.
Conclusion
Intelligent Electronic Devices are reshaping our world in exciting ways. From smarter homes to efficient factories, they’re making life easier and work more productive. As these devices evolve, they’ll bring new challenges in privacy and skills. But their benefits in efficiency, safety, and sustainability are clear. Embracing this technology wisely will help us build a better, smarter future for everyone.



![Beacons.ai A Complete Guide to the AI-Powered Link in Bio Platform [2024 Review]](https://techplces.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/Beacons.ai-A-Complete-Guide-to-the-AI-Powered-Link-in-Bio-Platform-2024-Review-300x157.jpg)






![Beacons.ai A Complete Guide to the AI-Powered Link in Bio Platform [2024 Review]](https://techplces.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/Beacons.ai-A-Complete-Guide-to-the-AI-Powered-Link-in-Bio-Platform-2024-Review-150x150.jpg)